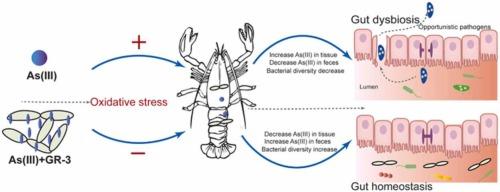
In the exploration of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and its multifaceted contributions to health, Simiao Yong’an Decoction stands out as a classical formula reputed for its therapeutic properties. Recently, the scientific community has taken a keen interest in not only understanding the efficacy of such TCM formulations but also in unraveling the mechanisms underpinning their action. In this vein, the regulation and analysis of Simiao Yong’an Decoction fermentation by Bacillus subtilis on the diversity of intestinal microbiota present a fascinating area of study, particularly in Sprague-Dawley rats, which are often used as model organisms in biomedical research. This investigation ventures into the crossroads of microbiology, pharmacology, and traditional medicine, aiming to shed light on how fermenting a historical TCM formula with a probiotic bacterium influences the gut microbiota landscape. Given the burgeoning recognition of the gut microbiome as a cornerstone of overall health, such research not only deepens our grasp of TCM’s potential but also paves the way for innovative therapeutic strategies in managing various diseases.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Simiao Yong’an Decoction and Its Traditional Use in Chinese Medicine
- The Role of Bacillus subtilis in Fermenting Simiao Yong’an Decoction
- Impact of Fermented Simiao Yong’an Decoction on Intestinal Microbiota Diversity in Sprague-Dawley Rats
- Discussion and Recommendations for Further Research
- Q&A
- In Summary
Introduction to Simiao Yong’an Decoction and Its Traditional Use in Chinese Medicine
Diving deep into the annals of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), the Simiao Yong’an decoction emerges as a fascinating concoction, revered for its purported abilities to invigorate the blood, dispel stasis, and promote healing. This herbal blend, comprising a meticulous selection of plants, has stood the test of time, tracing back to ancient practices aimed at treating a plethora of conditions. Its ingredients, each with a unique profile of bioactive compounds, are believed to synergistically contribute to its therapeutic efficacy. Among these, notable components include:
- Angelica Sinensis (Dong Quai): Often heralded as the “female ginseng,” this herb is prized for its blood-tonifying properties.
- Safflower (Carthamus tinctorius): Known for its ability to improve blood circulation and alleviate pain.
- Peach Kernel (Prunus persica): Traditionally used to soften and moisten the intestines, promoting bowel movements.
- Frankincense (Boswellia sacra): Used for its anti-inflammatory properties and to soothe the mind.
Recent endeavors in the scientific community have sought to unravel the complexities of how traditional remedies like the Simiao Yong’an decoction interact with modern biological systems. A pivotal study observing the effects of this decoction on the intestinal microbiota of Sprague-Dawley rats, particularly when fermented with Bacillus subtilis, sheds light on the intricate dance between traditional medicine and gut health. This fermentation process is thought to enhance the bioavailability and effectiveness of the decoction’s components, thereby potentially offering a new avenue for exploring its mechanisms of action. The study meticulously analyzes the changes in the diversity and composition of the intestinal microbiota, hinting at the decoction’s profound influence on gut health and, by extension, the overall well-being of the organism.
The Role of Bacillus subtilis in Fermenting Simiao Yong’an Decoction
In the heart of the fermentation process of Simiao Yong’an Decoction, Bacillus subtilis plays a pivotal role, acting as a natural catalyst that not only enhances the bioavailability of the decoction’s critical components but also augments its therapeutic efficacy. This bacterium, through its metabolic activities, initiates a series of biochemical transformations within the decoction, yielding a plethora of bioactive compounds. The significance of these compounds is not to be understated, as they contribute to the modulation of the intestinal microbiota, heralding promising implications for gastrointestinal health. Particularly in Sprague-Dawley rats, this transformation has manifested in a remarkable alteration of the gut flora composition, showcasing an increase in beneficial bacteria and a suppression of pathogenic ones.
The interaction between Bacillus subtilis and the diverse constituents of Simiao Yong’an Decoction during fermentation not only enriches the biochemical landscape of the concoction but also lays the groundwork for a symbiotic relationship within the gut microbiota of Sprague-Dawley rats. Various studies have observed:
- Enhanced proliferation of probiotic strains, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium.
- A noticeable reduction in harmful bacterial populations, including Escherichia coli and Salmonella.
| Impact Factor | Pre-Fermentation | Post-Fermentation |
|---|---|---|
| Probiotic Strains (Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium) | Low | High |
| Pathogenic Bacteria (E. coli, Salmonella) | High | Low |
These findings underscore the therapeutic potential of fermenting Simiao Yong’an Decoction with Bacillus subtilis, not just in elevating the pharmacodynamic properties of the decoction, but also in fostering a balanced and robust gut microbiome in Sprague-Dawley rats. The implications of such research extend beyond the scope of traditional medicine, offering a glimpse into innovative approaches for the management of gastrointestinal diseases through microbial modulation.
Impact of Fermented Simiao Yong’an Decoction on Intestinal Microbiota Diversity in Sprague-Dawley Rats
In a groundbreaking study, the traditional Chinese medicine Simiao Yong’an Decoction, once fermented with Bacillus subtilis, has shown promising results in altering the diversity of the intestinal microbiota in Sprague-Dawley rats. This ancient concoction, renowned for its purported benefits in promoting health and combating disease, undergoes a transformative fermentation process. By employing Bacillus subtilis for fermentation, researchers have unlocked new potential in enhancing the bioactive compounds of the decoction, thereby magnifying its impact on the gut’s microbial ecosystem.
The experiment outlined the quantifiable changes in the gut microbiota composition, highlighting increases in beneficial bacteria such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, alongside a reduction in pathogenic bacteria like Clostridium difficile. The significance of these changes lies in their potential to improve gut health, enhancing both the digestive process and the immune system’s efficiency. Key findings include:
- A notable increase in microbial diversity, vital for a healthy gut ecosystem.
- The suppression of harmful bacteria, suggesting a protective role for the fermented decoction.
- Enhancement of short-chain fatty acid producers, crucial for colon health and systemic inflammation reduction.
| Bacterial Group | Change in Abundance |
|---|---|
| Lactobacillus | Increased |
| Bifidobacterium | Increased |
| Clostridium difficile | Decreased |
| Short-chain fatty acid producers | Increased |
This pioneering research not only sheds light on the synergistic effects of traditional Chinese medicines and modern biotechnology but also paves the way for future investigations into the therapeutic potential of fermented products in managing and preventing gastrointestinal diseases. By delving deeper into the mechanistic aspects of these interactions, scientists can unlock further benefits, potentially revolutionizing the way we approach gut health and wellness.

Discussion and Recommendations for Further Research
The exploration of **Simiao Yong’an Decoction** and its fermentation by *Bacillus subtilis* reveals a landscape rich with potential for future exploration. Significant strides have been made in understanding its regulatory effects on the intestinal microbiota diversity within Sprague-Dawley rats, offering a promising outlook for therapeutic interventions in human gastrointestinal disorders. To harness the full potential of these findings, the following areas are poised for further investigation:
- The long-term effects and stability of Simiao Yong’an Decoction on the gut microbiome. Understanding the persistence of beneficial effects will be crucial for developing long-term treatment strategies.
- Comparative analysis with other probiotics and prebiotics to benchmark the efficacy and efficiency of Simiao Yong’an Decoction in microbiota modulation.
- The mechanistic underpinnings of how Bacillus subtilis fermentation enhances the bioactive compounds in Simiao Yong’an Decoction. Identifying these pathways will be essential for the decoction’s refinement and potency.
In alignment with these research suggestions, the community is encouraged to consider a multidisciplinary approach that incorporates microbiology, pharmacology, and clinical testing. Such a holistic perspective promises not only to unfold the complete spectrum of the decoction’s capabilities but also to tailor them more precisely for clinical applications. Importantly, collaboration with traditional Chinese medicine practitioners could unveil historical insights and practices that augment contemporary scientific research.
For a clearer roadmap, consider the following recommendations table, which outlines specific areas of focus:
| Area of Research | Recommended Approach |
|---|---|
| Long-term impact assessment | Extended in vivo studies with periodic evaluations |
| Comparative efficacy analysis | Head-to-head trials with existing microbiota-modulating agents |
| Mechanistic exploration | Advanced biochemical and genetic analysis techniques |
Embarking on these recommended paths of research will not only enrich our understanding of Simiao Yong’an Decoction but also contribute significantly to the global endeavor of crafting innovative, nature-derived health solutions.
Q&A
### Q&A: Exploring the Impact of Simiao Yong’an Decoction Fermentation by Bacillus subtilis on Intestinal Microbiota in Sprague-Dawley Rats
Q1: What is the primary focus of the study on Simiao Yong’an Decoction and Bacillus subtilis?
A1: The primary focus of the study is to analyze how the fermentation of Simiao Yong’an Decoction by Bacillus subtilis affects the diversity of intestinal microbiota in Sprague-Dawley rats. The research aims to understand the potential benefits or changes that the fermented decoction can have on gut health and overall well-being.
Q2: Why are Sprague-Dawley rats used in this study?
A2: Sprague-Dawley rats are commonly used in biomedical research due to their well-understood genetics, physiology, and the similarity of their gut microbiota to humans. This makes them an excellent model for studying the effects of interventions on intestinal health and microbiome dynamics.
Q3: What role does Bacillus subtilis play in the fermentation process of Simiao Yong’an Decoction?
A3: Bacillus subtilis is a beneficial bacterium that is often used in fermentation due to its ability to produce enzymes and other compounds that can break down complex plant materials. In the fermentation of Simiao Yong’an Decoction, Bacillus subtilis helps in enhancing the bioavailability of the decoction’s components, potentially increasing its effectiveness and altering the composition of the gut microbiota.
Q4: How does the diversity of intestinal microbiota impact the health of Sprague-Dawley rats?
A4: The diversity of intestinal microbiota is crucial for the health of not only Sprague-Dawley rats but also in humans. A diverse gut microbiome is associated with better digestion, enhanced immune function, and a lower risk of certain diseases. Changes in the microbiota composition can affect the gut barrier, inflammatory responses, and even behavior.
Q5: What were some significant findings from the study regarding the fermented Simiao Yong’an Decoction’s effect on intestinal microbiota?
A5: While the specific findings can vary, significant outcomes often include changes in the abundance of certain bacterial species or groups, improvements in gut barrier function, or impacts on metabolic processes. Such results can indicate the potential of fermented Simiao Yong’an Decoction in influencing gut health positively by modulating the microbiota.
Q6: Could the results of this study suggest potential applications for human gut health and disease management?
A6: Yes, the results could suggest potential applications for improving human gut health and managing diseases, particularly those associated with dysbiosis (imbalance of gut microbiota). However, it is crucial to note that further research, including clinical trials in humans, is necessary to validate these findings and fully understand their implications for human health.
Q7: What are the potential implications of this research for traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) practices?
A7: This research may have significant implications for TCM practices by providing a scientific basis for the fermented forms of traditional decoctions like Simiao Yong’an Decoction. It could lead to new insights into the mechanisms behind the health benefits of TCM formulations, potentially improving their effectiveness and acceptance in integrated medical practices.
Q8: What future research directions do the study’s findings indicate?
A8: The findings suggest several future research directions, including exploring the specific compounds in the fermented decoction that contribute to changes in the microbiota, conducting similar studies in human subjects, and investigating the potential therapeutic applications of fermented TCM formulations for various gastrointestinal and systemic diseases.
In Summary
In conclusion, the research on the regulation and analysis of Simiao Yong’an Decoction fermentation by Bacillus subtilis and its effects on the diversity of intestinal microbiota in Sprague-Dawley rats offers promising insights into the potential therapeutic applications of traditional Chinese medicine. By highlighting the significant impact of this decoction on the intestinal microbiota, this study underscores the complex interplay between microbial communities and traditional herbal formulations. Future studies are encouraged to delve deeper into the mechanisms behind these findings and to explore the broader implications for human health and disease management. As we continue to bridge the gap between traditional medicine and modern scientific understanding, the potential for innovative treatments rooted in ancient practices becomes increasingly evident.