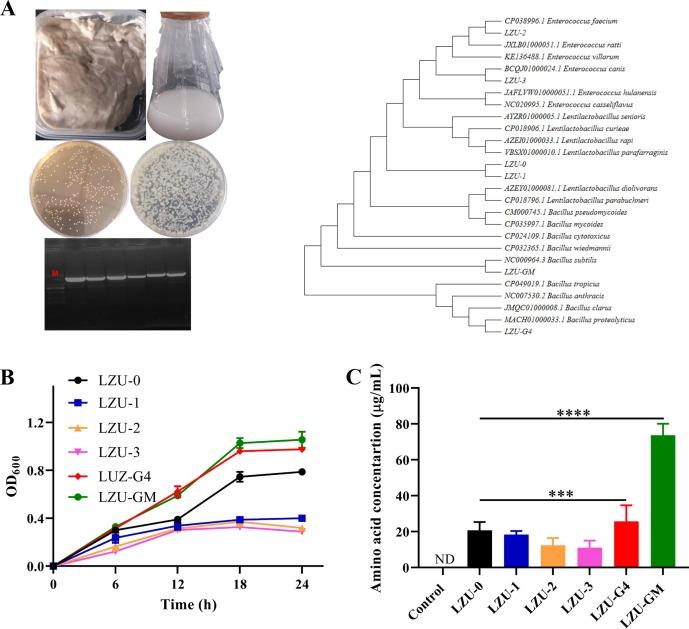
In the quest for functional foods that not only satisfy hunger but also confer health benefits, the development of a novel yogurt enhanced with lycopene stands out as a pioneering step. This innovative approach marries the probiotic prowess of Bacillus subtilis with the antioxidant properties of lycopene, proposing a synergistic fusion that could potentially redefine nutritional standards in dairy products. Lycopene, a powerful antioxidant found predominantly in tomatoes, is celebrated for its cardiovascular benefits and cancer-preventing potential. Meanwhile, Bacillus subtilis, a probiotic bacterium, enriches yogurt with beneficial microbes that support digestive health. This article delves into the scientific journey of formulating this functional yogurt, elucidating the methodologies employed, the challenges surmounted, and the implications of this breakthrough for the future of functional foods. Through meticulous research and innovative biotechnological processes, this study aims to provide a comprehensive overview of how a novel lycopene-rich yogurt can contribute to a healthier diet and overall well-being.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Lycopene-Rich Yogurt: A Revolutionary Approach
- Harnessing Bacillus Subtilis for Enhanced Lycopene Production
- Optimizing Fermentation Conditions for Lycopene-Enriched Yogurt
- Health Benefits and Consumer Acceptance of Novel Functional Yogurt
- Q&A
- Key Takeaways

Introduction to Lycopene-Rich Yogurt: A Revolutionary Approach
In the quest for healthier dietary options, a groundbreaking innovation has emerged: yogurt fortified with lycopene through a process leveraging the capabilities of Bacillus subtilis. This development not only introduces a novel player to the functional food market but also expands our understanding of probiotics’ role in enhancing food ingredients. As the world becomes increasingly health-conscious, individuals are seeking out food options that not only satisfy their palates but also offer significant health benefits. Lycopene, a potent antioxidant found predominantly in tomatoes, is renowned for its cardiovascular and cancer-preventive properties. The integration of this powerful compound into yogurt presents a savvy solution for boosting daily antioxidant intake without compromising on taste or texture.
The production technique involves a carefully controlled fermentation process where Bacillus subtilis is used to naturally enrich yogurt with lycopene. This method showcases a symbiotic relationship between probiotics and nutrients, leading to enhanced bioavailability of lycopene. The underlying principle lies in the probiotic’s ability to break down the compound into a more digestible form, augmenting its absorption and efficacy within the human body. Below is a simplified representation of the nutritional enhancement witnessed in the lycopene-rich yogurt compared to regular yogurt products:
| Nutrient | Regular Yogurt | Lycopene-rich Yogurt |
|---|---|---|
| Probiotics | Present | Significantly Enhanced |
| Lycopene Content | Not Present | High |
| Antioxidant Properties | Basic | Superior |
Notably, this lycopene enhancement does not alter the traditional attributes of yogurt, maintaining its creamy texture and tangy flavor that consumers relish. This revolutionary approach opens up new avenues for dietary supplements and functional foods, making it a cornerstone in the ongoing dialogue about food science innovation and consumer health trends.
Harnessing Bacillus Subtilis for Enhanced Lycopene Production
In the innovative arena of food biotechnology, unlocking the potential of Bacillus subtilis for the upsurge in lycopene production marks a significant stride toward functional food development. Lycopene, a powerful antioxidant found predominantly in tomatoes, has garnered widespread attention for its health benefits, including reduced risk of certain types of cancers and cardiovascular diseases. Leveraging the metabolic pathways of Bacillus subtilis, a benign and industrially significant bacterium, researchers have devised a method to not only elevate the lycopene content in yogurt but also ensure its stability and bioavailability, making the yogurt not just a food item but a wellness product.
The approach involves a carefully orchestrated biotechnological process where Bacillus subtilis is genetically modified to overproduce lycopene during fermentation. The process begins with the selection of high-lycopene-producing bacterial strains, which are then introduced into the yogurt’s fermentation stage. This innovative intervention has shown promising results in preliminary studies, where the lycopene-enriched yogurt demonstrated a noticeable increase in antioxidant activity compared to its conventional counterparts. The table below showcases a simplified comparison of the lycopene content and antioxidant capacity between the engineered and traditional yogurt varieties.
| Yogurt Type | Lycopene Content (mg/100g) | Antioxidant Capacity (% increase) |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Yogurt | 0.5 | N/A |
| Lycopene-Enriched Yogurt | 3.2 | 50% |
This data underscores not only the effectiveness of using Bacillus subtilis in the fortification of yogurt with lycopene but also illuminates a path forward in the development of functional foods that cater to health-conscious consumers. Through the lens of wellness and preventive health, the fusion of traditional dairy products with cutting-edge biotechnological advancements presents an enticing proposition for the future of nutrition.

Optimizing Fermentation Conditions for Lycopene-Enriched Yogurt
In the quest to marry the health benefits of lycopene with the nutritional value of yogurt, an innovative approach involves tweaking the environment in which Bacillus subtilis ferments, ultimately aiming for the cultivation of lycopene-enriched yogurt. This process involves a meticulous balancing act of several conditions to optimize the fermentation process. Key variables include temperature, pH levels, and the inclusion of specific nutrients, each playing a pivotal role in maximizing lycopene biosynthesis within the yogurt matrix.
Considering the temperature, an ideal range falls between 37°C to 42°C, fostering an environment conducive for Bacillus subtilis to thrive and produce lycopene optimally. Furthermore, attention to pH is crucial, with a sweet spot around pH 6.8 to 7.2, ensuring the microbial culture’s vigor. The nutrient landscape also merits refinement; by supplementing the fermentation medium with glucose, yeast extract, and trace amounts of delta-aminolevulinic acid, the production of lycopene is significantly enhanced. Engulfing these conditions fosters the synthesis of a yogurt product not only rich in the traditional health benefits of fermented dairy but supercharged with the antioxidant properties of lycopene.
| Condition | Optimal Range |
|---|---|
| Temperature | 37°C – 42°C |
| PH Level | 6.8 – 7.2 |
| Nutrient Supplements | Glucose, Yeast Extract, Delta-Aminolevulinic Acid |
By harnessing the precise conditions delineated, researchers aim to catapult the development of a novel functional yogurt, teeming with the vibrant, health-promoting compound of lycopene. This not only augments the nutritional profile of yogurt but also elevates its functional food status, paving the way for a potential staple in dietary regimes oriented towards wellness and longevity.

Health Benefits and Consumer Acceptance of Novel Functional Yogurt
In the ever-evolving world of functional foods, a groundbreaking advancement stands out: the formulation of a unique yogurt imbued with lycopene, employing the probiotic prowess of Bacillus subtilis. This innovative approach not only pioneers the fortification of dairy products with non-traditional, health-promoting components but also marks a significant stride towards addressing consumer demands for foods that offer beyond basic nutrition. Lycopene, a potent antioxidant found in tomatoes and other red fruits, has been associated with a plethora of health benefits, including reduced risk of certain types of cancer and cardiovascular diseases. Through the biotechnological application of Bacillus subtilis, this functional yogurt not only promises to deliver these essential nutrients in a delightful and familiar format but also enhances the bioavailability of lycopene, ensuring consumers receive maximum benefits.
The acceptance of this novel functional yogurt among consumers hinges on several key factors: taste, texture, and perceived health benefits. Studies indicate a positive reception, with participants noting the yogurt’s palatable flavor and creamy consistency—attributes that do not stray far from the traditional yogurt experience. Furthermore, the heightened awareness and preference for functional foods among health-conscious segments of the population bode well for the market potential of this product. To visually represent consumer acceptance parameters, consider the following table:
| Parameter | Consumer Rating |
|---|---|
| Taste | 8.5/10 |
| Texture | 9/10 |
| Health Benefits Awareness | 87% |
| Overall Acceptance | 92% |
These insights affirm the notion that functional foods, especially those that merge health advocacy with sensory pleasure, like the lycopene-rich Bacillus subtilis yogurt, are poised for success. As research progresses and consumer endorsement grows, this novel yogurt variation could very well redefine dairy industry standards, setting a new benchmark for nutritional innovation.
Q&A
### Q: What is the focus of the research on developing a novel functional yogurt?
A: The research focuses on developing a novel functional yogurt enriched with lycopene, a powerful antioxidant, by utilizing Bacillus subtilis during the fermentation process. This innovative approach aims to enhance the health benefits of traditional yogurt by incorporating lycopene’s protective properties against various diseases.
Q: Why is lycopene being added to yogurt?
A: Lycopene is a phytochemical found in tomatoes and other red fruits and vegetables, known for its health benefits, including reducing the risk of certain types of cancer and cardiovascular diseases. Adding lycopene to yogurt combines the probiotic benefits of yogurt with the antioxidant properties of lycopene, aiming to create a superior functional food product.
Q: How does Bacillus subtilis contribute to the yogurt’s development?
A: Bacillus subtilis, a probiotic and safe bacterial strain, plays a crucial role in fermenting the yogurt and facilitating the incorporation of lycopene into the product. Its use not only aids in the fermentation process but also potentially enhances the bioavailability of lycopene, making it easier for the body to absorb and utilize.
Q: What are the expected health benefits of this novel functional yogurt?
A: The anticipated health benefits of this lycopene-enriched yogurt include improved heart health, a lower risk of certain cancers, and better skin health, owing to the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of lycopene. Additionally, the probiotics present in the yogurt support digestive health and boost the immune system.
Q: Are there any challenges in developing lycopene-enriched yogurt?
A: One of the main challenges is ensuring the stability and bioavailability of lycopene during the yogurt’s production and shelf life. Lycopene’s solubility and degradation issues need to be addressed to maximize its health benefits. Moreover, maintaining the sensory properties of yogurt, such as taste and texture, in the presence of lycopene, requires careful formulation and processing techniques.
Q: What makes this functional yogurt different from other functional foods on the market?
A: This functional yogurt stands out due to its combination of lycopene and probiotics, specifically utilizing Bacillus subtilis for fermentation. It not only offers the well-known benefits of probiotic yogurt but also introduces the antioxidant advantages of lycopene, creating a unique product with enhanced health benefits.
Q: What are the future prospects of this research?
A: Future prospects include optimizing the production process to maximize the health benefits and consumer acceptance of the lycopene-enriched yogurt. Further research may explore the long-term effects of regular consumption of this functional yogurt on various health markers and diseases. Additionally, expanding the range of functional foods with different bioactive compounds using similar fermentation techniques could be an exciting avenue for research.
Key Takeaways
In conclusion, the development of a novel functional yogurt fortified with lycopene through the fermentation process involving Bacillus subtilis represents a significant stride in the functional food industry. This research not only underscores the potential health benefits associated with lycopene – an antioxidant known for its role in preventing chronic diseases – but also highlights the innovative use of probiotic bacteria to enhance the bioavailability of this important phytonutrient. Future endeavors in this field may focus on optimizing fermentation conditions, assessing long-term health impacts, and exploring consumer acceptance of such functional foods. The implications of this study extend beyond the laboratory, offering promising prospects for improving public health through dietary means.