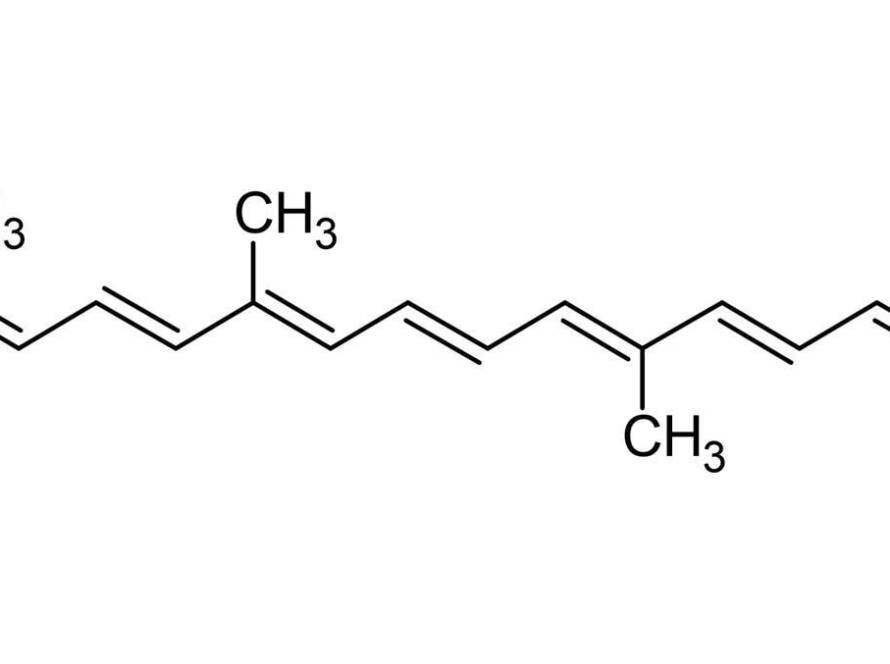
In the quest for innovative treatments for autoimmune diseases, scientists are exploring the therapeutic potentials of natural products and their bioactive components. One such avenue of research has led to the intriguing prospect of utilizing camel milk, supplemented with Bacillus amyloliquifaciens, as a potential intervention for neuroinflammation in autoimmune encephalomyelitis. This condition, serving as a model for multiple sclerosis, involves complex immune-mediated processes that damage the central nervous system. Given the intricate interplay of genetic, environmental, and immunological factors in autoimmune diseases, novel approaches that can modulate the immune response hold great promise. This article delves into a recent study that investigates how a specific probiotic-augmented camel milk formulation impacts the regulation of inflammatory markers in a mouse model, potentially paving the way for new therapeutic strategies in the management of neuroinflammatory conditions.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Role of Bacillus amyloliquifaciens in Camel Milk for Neuroinflammatory Suppression
- Mechanisms of Action: How Bacillus amyloliquifaciens Affects Inflammatory Markers in Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis
- Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Camel Milk Supplementation in Neuroinflammatory Conditions
- Recommendations for Further Research and Clinical Trials on Camel Milk and Bacillus amyloliquifaciens Supplements
- Q&A
- Closing Remarks
Understanding the Role of Bacillus amyloliquifaciens in Camel Milk for Neuroinflammatory Suppression
In the quest to find innovative and natural solutions for managing neuroinflammation, a groundbreaking study shines a spotlight on an unexpected hero: Bacillus amyloliquifaciens-supplemented camel milk. Packed with unique properties, camel milk, when enhanced with this particular probiotic strain, presents a fascinating avenue for therapeutic intervention against autoimmune encephalomyelitis, a model often used to mimic human multiple sclerosis. The duo works in tandem not just to nourish the body but to wield a powerful influence over the tides of inflammation, essentially reprogramming the immune response to deter the progression of neuroinflammation.
The mechanism by which Bacillus amyloliquifaciens and camel milk exert their effect is a complex ballet of biochemical interactions. At the heart of this interaction is the regulation of inflammatory markers; cytokines such as IL-10 and TNF-alpha, known for their role in inflammation and immune responses, are modulated, thus hinting at the probiotic’s potential to orchestrate a reduction in neuroinflammation. In essence, the synergistic effect of the probiotic-supplemented milk on these markers illuminates a path forward where neuroinflammatory diseases could be managed more effectively with fewer side effects compared to conventional pharmacological interventions.
Mechanisms of Action: How Bacillus amyloliquifaciens Affects Inflammatory Markers in Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis
In the fascinating realm of microbiology and immunotherapy, **Bacillus amyloliquifaciens**, a probiotic bacterium, has shown promising effects when used in conjunction with camel milk to mitigate neuroinflammation in autoimmune encephalomyelitis. This condition, a mouse model simulating multiple sclerosis in humans, involves complex immunological mechanisms that lead to inflammation and damage in the central nervous system. The supplemented camel milk acts as a vehicle that not only delivers the bacterium efficiently but also enhances its therapeutic potential due to camel milk’s unique composition. This combined approach targets neuroinflammation through several mechanisms, altering the course of the autoimmune response in a beneficial manner.
First and foremost, the interaction between Bacillus amyloliquifaciens and the immune system results in a modulation of inflammatory markers. These markers, including cytokines like IFN-γ (Interferon gamma) and TNF-α (Tumor Necrosis Factor alpha), play critical roles in propagating inflammation and autoimmune responses. By reducing the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and increasing anti-inflammatory ones, such as IL-10 (Interleukin-10), the treatment can effectively attenuate inflammation. Moreover, this probiotic intervention stimulates regulatory T cells, pivotal in maintaining immune balance, thereby preventing overactivation and further inflammation. Additionally, the bacterium’s role in enhancing gut barrier function could also contribute to its neuroprotective effects, given the emerging evidence linking gut health to neuroinflammation. The table below succinctly highlights the key inflammatory markers modulated by the treatment:
<table class="wp-table">
<tr>
<th>Inflammatory Marker</th>
<th>Effect of Treatment</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>IFN-γ</td>
<td>Decreased</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>TNF-α</td>
<td>Decreased</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>IL-10</td>
<td>Increased</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Regulatory T Cells</td>
<td>Stimulated</td>
</tr>
</table>This innovative approach, blending microbiology with nutritional science, opens new vistas in the treatment of autoimmune diseases, particularly those affecting the nervous system. The ability of Bacillus amyloliquifaciens supplemented camel milk to regulate key inflammatory markers offers a ray of hope for individuals suffering from conditions akin to multiple sclerosis, paving the way for more natural, symbiotic therapies in managing autoimmune disorders.
Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Camel Milk Supplementation in Neuroinflammatory Conditions
In the realm of functional foods, camel milk has garnered attention for its unique nutritional profile and potential health benefits. Recent studies have delved into its bioactive components, particularly when enhanced with Bacillus amyloliquifaciens, a probiotic known for its anti-inflammatory properties. This novel supplementation approach was explored as a potential therapeutic intervention for neuroinflammatory conditions, such as autoimmune encephalomyelitis, a model closely mirroring human multiple sclerosis. Through meticulous research, it was observed that this fortified camel milk significantly dampened the inflammatory response in the central nervous system (CNS), showcasing a promising avenue for dietary strategies in managing neuroinflammation.
Key findings from the study highlighted several mechanisms through which Bacillus amyloliquifaciens-supplemented camel milk exerted its beneficial effects:
- **Down-regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines:** The supplemented milk led to a marked decrease in the levels of cytokines like IFN-γ and TNF-α, which are known to play pivotal roles in the pathogenesis of neuroinflammatory diseases.
- **Up-regulation of anti-inflammatory markers:** Conversely, there was an increase in anti-inflammatory markers, supporting the body’s ability to counteract inflammatory responses more effectively.
- **Modulation of gut microbiota:** The probiotic component of the supplementation was found to positively influence the gut-brain axis, further contributing to the anti-inflammatory effects observed.
| Marker | Control Group | Supplemented Group |
|---|---|---|
| IFN-γ | High | Low |
| TNF-α | High | Low |
| Anti-inflammatory markers | Low | High |
These findings not only underscore the potential therapeutic application of camel milk supplementation but also pave the way for further research into dietary interventions for neurodegenerative and neuroinflammatory conditions. As we continue to unravel the complexities of the gut-brain axis and its role in immune modulation, functional foods like camel milk, especially when enhanced with probiotics, offer a compelling area for innovation and therapeutic exploration.
Recommendations for Further Research and Clinical Trials on Camel Milk and Bacillus amyloliquifaciens Supplements
Given the intriguing findings from the recent study on the effects of Bacillus amyloliquifaciens-supplemented camel milk on neuroinflammation in a mouse model, it’s imperative that the scientific community delves deeper into the synergistic role these components play not just in neuroinflammatory conditions but across a broader spectrum of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. To propel our understanding forward, here are recommendations for future research directives and clinical trials that could illuminate new pathways for therapeutic interventions.
- **Expand the scope of investigation**: Future studies should explore the impact of Bacillus amyloliquifaciens-supplemented camel milk on other models of neuroinflammatory and autoimmune disorders beyond autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Implementing varied dosages and treatment durations would provide invaluable insights into the efficacy and safety profile of this novel intervention.
- **Clinical trials in human subjects**: Initiating clinical trials to assess the effects of this supplementation in humans suffering from similar neuroinflammatory conditions is crucial. These trials should be meticulously designed to measure the improvements in specific biomarkers of inflammation, patient-reported symptom relief, and any potential adverse reactions.
- **Investigate the mechanistic pathways**: There’s a strong need for studies aimed at deciphering the underlying mechanisms through which Bacillus amyloliquifaciens and camel milk exert their anti-inflammatory effects. Such research could involve genomic, proteomic, and metabolomic approaches to uncover the molecular interactions at play.
The journey towards establishing Bacillus amyloliquifaciens-supplemented camel milk as a viable therapeutic option for neuroinflammation and other related conditions is still in its infancy. However, by following these recommendations for further research and clinical trials, the scientific community has the potential to unlock a treasure trove of knowledge that could lead to breakthroughs in the treatment of these challenging diseases. The promise shown in initial studies serves as a beacon, guiding the way towards innovative solutions that harness the natural synergy between microorganisms and milk from unique sources like camels.
Q&A
### Q&A: Understanding the Effects of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens-Supplemented Camel Milk on Neuroinflammation in Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis
Q1: What is autoimmune encephalomyelitis and why is it significant?
Autoimmune encephalomyelitis is an inflammation-based model of the central nervous system, often used to study multiple sclerosis and similar neurological autoimmune diseases. Its significance lies in its ability to shed light on the mechanisms behind neuroinflammation and the potential pathways for therapeutic intervention in autoimmune disorders affecting the brain.
Q2: What role does Bacillus amyloliquefaciens play in managing neuroinflammation?
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, a probiotic bacterium, has been identified for its anti-inflammatory properties. In the context of autoimmune encephalomyelitis, it is believed that the bacterium can regulate inflammatory markers, thus helping to suppress neuroinflammation. This effect may stem from its ability to modulate the gut microbiota, which in turn impacts immune responses and inflammation throughout the body, including the central nervous system.
Q3: How does camel milk come into play, and why use it as a supplement?
Camel milk has been cited for its numerous health benefits, including anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and immunomodulatory effects. Its unique composition, which is different from other types of milk, makes it an excellent vehicle for delivering probiotics like Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. By supplementing camel milk with this bacterium, researchers aim to enhance its natural beneficial properties and potentially amplify its positive effects on neuroinflammation.
Q4: What were the primary findings of the study on camel milk supplementation in a mouse model?
The study found that supplementation of camel milk with Bacillus amyloliquefaciens significantly suppressed neuroinflammation in a mouse model of autoimmune encephalomyelitis. This was evidenced by reduced levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and increased levels of anti-inflammatory cytokines in the mice. Additionally, there was decreased demyelination and infiltration of inflammatory cells in the central nervous system, indicating a protective effect against autoimmune attacks.
Q5: How might these findings impact future treatments for neuroinflammatory and autoimmune diseases?
These findings suggest that Bacillus amyloliquefaciens-supplemented camel milk could offer a novel dietary approach to managing neuroinflammation and potentially ameliorate symptoms of autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis. While further research is needed to translate these results to humans, this study offers a promising foundation for exploring functional foods in the context of neuroimmune disorders.
Q6: What are the limitations of this study, and what future research is suggested?
The study’s limitations include its reliance on a mouse model, which while informative, cannot fully replicate the complexity of human neuroimmune interactions. Additionally, the exact mechanisms through which Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and camel milk exert their effects require further elucidation. Future research should aim to explore these mechanisms in greater detail, as well as conduct clinical trials to assess the safety, efficacy, and therapeutic potential of this approach in humans.
These questions and answers delve into the promising research on the potential benefits of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens-supplemented camel milk for suppressing neuroinflammation in autoimmune conditions, paving the way for further exploration in the field of dietary intervention for neuroimmune disorders.
Closing Remarks
In conclusion, the study on Bacillus amyloliquefaciens-supplemented camel milk and its impact on neuroinflammation in a mouse model of autoimmune encephalomyelitis opens a new chapter in the field of neuroimmunology and functional foods. By systematically elucidating the mechanisms through which this novel intervention regulates inflammatory markers and suppresses neuroinflammation, the research not only enriches our understanding of the intricate interactions between diet, gut microbiota, and immune responses but also underscores the potential of leveraging naturally occurring compounds in dietary interventions for neurological conditions. The findings advocate for further exploration into the therapeutic applications of probiotics and functional foods in managing autoimmune disorders, serving as a stepping stone for future clinical studies. It is clear that the journey to fully harness the potential of such dietary interventions in clinical practice is complex and requires a multidisciplinary approach. Nonetheless, this study paves the way for innovative strategies in the prevention and management of neuroinflammatory diseases, highlighting the significance of diet-microbiome-immune axis in maintaining neurological health and well-being.