In the intricate dance of the human gut microbiome, where countless microorganisms participate in the maintenance and modulation of our health, the potential therapeutic roles of specific probiotic strains have captivated the scientific community. Among these, the Limosilactobacillus fermentum species, derived from fermented foods, emerges as a focal point of interest, particularly for its immunomodulatory effects and potential implications for treating environmental enteropathy—a malabsorption syndrome primarily affecting populations in low-resource settings. This article delves into the sophisticated mechanisms through which L. fermentum influences the immune system and gut microbiota, offering insights into its potential as a natural, dietary intervention in the context of environmental enteropathy. By unraveling the science behind the probiotic properties of L. fermentum strains, this exploration not only underscores the significance of dietary choices in gut health but also illuminates a promising avenue for alleviating the burden of intestinal disorders on a global scale.
Table of Contents
- Unlocking the Secrets of Limosilactobacillus fermentum: A Key Player in Fermented Foods
- The Immunomodulatory Power of Fermented Food-Derived Probiotics in Combating Environmental Enteropathy
- Practical Dietary Recommendations for Incorporating Fermented Foods Rich in Limosilactobacillus fermentum
- Q&A
- Insights and Conclusions
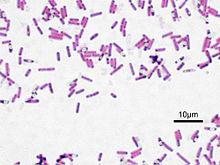
Unlocking the Secrets of Limosilactobacillus fermentum: A Key Player in Fermented Foods
The exploration of Limosilactobacillus fermentum strains derived from fermented foods has unveiled significant potential in the realm of probiotics, especially concerning their immunomodulatory effects. This bacterium, found abundantly in various fermented foods, is gaining attention for its role in not only enhancing gut health but also in fortifying the immune system. Research suggests that these strains can modulate gut microbiota, improving barrier function and reducing inflammation, which is crucial in battling environmental enteropathy—a condition prevalent in areas with poor sanitation and hygiene. The significance of these findings lies in the potential to develop targeted probiotic interventions that can alleviate the symptoms of this condition and improve the quality of life for affected populations.
Studies have shown that the introduction of **Limosilactobacillus fermentum** into the diet can lead to:
- **Enhanced gut barrier integrity**: Strengthening the intestinal barrier, thus preventing the intrusion of harmful pathogens.
- **Modulation of the immune system**: Influencing both innate and adaptive immune responses to foster a more resilient defense mechanism against infections.
- **Reduction of inflammation**: Lowering systemic inflammation levels, which is particularly beneficial for individuals suffering from chronic inflammatory conditions.
These attributes highlight the therapeutic potential of **Limosilactobacillus fermentum** in managing and preventing diseases related to impaired gut functionality and compromised immune systems. Further research into the specific mechanisms through which these strains exert their beneficial effects could pave the way for novel probiotic formulations, offering a natural and sustainable approach to enhancing human health and well-being.
The Immunomodulatory Power of Fermented Food-Derived Probiotics in Combating Environmental Enteropathy
In the realm of gut health and disease prevention, the spotlight increasingly shines on the novel benefits of Limosilactobacillus fermentum, a probiotic powerhouse found abundantly in fermented foods. This bacterium, through its complex biochemical pathways, orchestrates a symphony of immunomodulatory effects, making it a subject of keen interest for researchers exploring treatments for environmental enteropathy—a pervasive condition in regions beset by poor sanitation and hygiene. Environmental enteropathy, characterized by chronic inflammation of the intestines, impairs nutrient absorption and compromises the immune system, setting the stage for a myriad of health issues. However, the bioactive compounds produced by L. fermentum during fermentation exhibit the potential to strengthen intestinal barriers, modulate gut flora, and ignite immune response mechanisms that can counteract the malabsorption and immunodeficiency inflicted by this condition.
The dialogue concerning the immunomodulatory prowess of L. fermentum encompasses various mechanisms, including the modulation of gut microbiota composition, the enhancement of intestinal barrier function, and the elicitation of anti-inflammatory and anti-pathogenic responses. These processes collectively contribute to an intestinal environment that is less hospitable to the pathogens responsible for environmental enteropathy. To illustrate, recent studies elucidate how:
- L. fermentum can increase the production of tight junction proteins, fortifying the gut barrier against pathogenic infiltration.
- Through the secretion of bacteriocins and organic acids, it exerts a direct antimicrobial effect against common intestinal pathogens.
- It stimulates the body’s immune cells, such as dendritic cells and macrophages, enhancing the gut’s defensive responses and possibly leading to improved vaccine efficacy.
These insights indicate not only a promising avenue for mitigating the symptoms of environmental enteropathy but also highlight the broader potential of fermented food-derived probiotics in fostering gut health and immunological balance.

Practical Dietary Recommendations for Incorporating Fermented Foods Rich in Limosilactobacillus fermentum
Integrating fermented foods into one’s diet that are rich in Limosilactobacillus fermentum strains calls for a thoughtful selection of ingredients and meals that resonate with both the palate and health objectives. These strains, noteworthy for their probiotic properties and immunomodulatory effects, can be found in a variety of naturally fermented foods. Consider the inclusion of foods like kimchi, sauerkraut, kefir, and traditional yogurts. These not only provide a rich source of beneficial bacteria but also enhance flavor profiles in daily meals. For optimal benefit, it is advisable to consume these foods in their uncooked form, as the heat can diminish the potency of the probiotic strains.
<p>Indeed, incorporating these foods into your diet doesn’t have to feel like a chore—a touch of creativity can turn this nutritional endeavor into an exciting culinary journey. Start your day with a smoothie blended with kefir and a medley of fruits, introduce a side of sauerkraut with your lunch, or top your salads with a generous dollop of traditional yogurt. For those with a preference for Asian cuisine, integrating kimchi into dishes not only boosts the food's nutritional profile but also adds a zestful flavor. It’s imperative to aim for moderation and variety, as excessive consumption of fermented foods can lead to gastrointestinal discomfort in some individuals.</p>
Q&A
### Harnessing the Probiotic Properties and Immunomodulatory Effects of Fermented Food-Derived Limosilactobacillus fermentum Strains: Implications for Environmental Enteropathy
Q&A Section
Q1: What are Limosilactobacillus fermentum strains, and how are they sourced?
A1: Limosilactobacillus fermentum strains are a species of bacteria that are commonly found in various fermented foods. These strains are sourced from the fermentation process of food items like yogurt, sauerkraut, and kimchi. They are known for their probiotic properties, which can aid in the digestion process and improve gut health.
Q2: What is environmental enteropathy, and who is most affected by it?
A2: Environmental enteropathy, also known as tropical enteropathy, is a condition characterized by inflammation of the intestine, primarily due to poor sanitary conditions and chronic exposure to enteric pathogens. This condition disproportionately affects individuals in developing countries, especially children, contributing to malnutrition and impaired growth.
Q3: How do the probiotic properties of Limosilactobacillus fermentum strains combat environmental enteropathy?
A3: The probiotic properties of Limosilactobacillus fermentum strains help in several ways. These bacteria can strengthen the gut barrier, reduce inflammation, and promote a healthy balance of gut microbiota. By doing so, they can mitigate the impacts of environmental enteropathy, such as nutrient malabsorption and chronic diarrhea.
Q4: What are the immunomodulatory effects of Limosilactobacillus fermentum strains?
A4: The immunomodulatory effects of Limosilactobacillus fermentum strains include boosting the immune system’s ability to combat pathogens while regulating its response to prevent excessive inflammation. These effects are crucial for maintaining intestinal health and addressing the underlying systemic inflammation associated with environmental enteropathy.
Q5: What implications do these findings have for public health strategies in regions affected by environmental enteropathy?
A5: The findings suggest that incorporating fermented food-derived Limosilactobacillus fermentum strains into the diet may offer a practical and cost-effective strategy to combat environmental enteropathy in affected regions. Public health strategies could include promoting the production and consumption of fermented foods as a dietary supplement to improve gut health and reduce the incidence of enteropathy-related diseases.
Q6: Are there any potential risks or drawbacks to increasing the intake of fermented foods containing Limosilactobacillus fermentum for individuals with environmental enteropathy?
A6: While fermented foods containing Limosilactobacillus fermentum are generally considered safe for most people, individuals with compromised immune systems or pre-existing gastrointestinal conditions should consume them with caution. Overconsumption may lead to gastrointestinal discomfort or adverse reactions in susceptible individuals. It is essential to consult healthcare professionals before making significant dietary changes, especially in individuals with environmental enteropathy.
Insights and Conclusions
In conclusion, the exploration of fermented food-derived Limosilactobacillus fermentum strains presents a promising frontier in the battle against environmental enteropathy, a condition that continues to challenge global health systems, particularly in developing countries. Through the lens of our investigation, we have uncovered not only the probiotic properties of these strains but also their potential immunomodulatory effects, which could be crucial in mitigating the impacts of environmental enteropathy. It is evident that integrating these findings into practical applications requires a multidisciplinary approach, blending traditional knowledge with advanced scientific research.
As we move forward, it is vital that further studies are conducted to deepen our understanding of the intricate mechanisms through which Limosilactobacillus fermentum exerts its beneficial effects. Such research should not only focus on the biochemical pathways involved but also consider the environmental and dietary factors that influence the efficacy of these probiotic strains. Collaboration between microbiologists, nutritionists, and medical professionals will be key in translating these findings into effective therapeutic strategies that can be deployed in real-world settings.
The journey from bench to bedside is often long and fraught with challenges. However, the potential rewards of harnessing the power of Limosilactobacillus fermentum for improving human health are immense. By continuing to unravel the complexities of these probiotic strains and their interaction with the human immune system, we can open new avenues for the prevention and management of environmental enteropathy, ultimately contributing to the enhancement of global health outcomes.