In the rapidly evolving field of dietary science, understanding the interaction between food components and gut microbiota has become pivotal in mitigating adverse health effects and promoting overall well-being. A groundbreaking study reveals the potential of Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM, a gluten-degrading probiotic, in revolutionizing the approach towards managing and alleviating the detrimental impact of gluten additives in food. Through meticulous research, this study showcases the capability of Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM not only to degrade gluten effectively but also to harmonize the gut microbiota in mice, suggesting promising implications for humans struggling with gluten-related disorders. This exploration taps into the intricate dynamics between dietary gluten, gut health, and microbiota balance, shedding light on innovative interventions that could redefine dietary guidelines and therapeutic strategies for individuals sensitive to gluten.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Role of Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM in Gluten Digestion
- Exploring the Impact of Gluten Additive Food on Mice and the Mitigating Effects of Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM
- Recommendations for Incorporating Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM Probiotics to Support Gut Health and Gluten Tolerance
- Analyzing the Effects of Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM on Gut Microbiota Balance in Gluten-Fed Mice
- Q&A
- Closing Remarks

Understanding the Role of Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM in Gluten Digestion
In the realm of nutritional science, the quest for solutions that mitigate the adverse reactions caused by gluten consumption has led to remarkable discoveries. Among these, the probiotic Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM stands out as a beacon of hope. This remarkable strain has shown a unique ability to degrade gluten peptides, which are typically resistant to the digestive enzymes produced by humans. The process unfolds in the gut, where LZU-GM breaks down gluten molecules before they can trigger the harmful inflammatory responses seen in individuals with gluten sensitivities or celiac disease. Furthermore, its efficacy was observed in detailed studies, showing a significant reduction in the markers of gluten-induced distress in mice models.
The implications of these findings are vast. For one, they hint at the potential of Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM as a natural dietary supplement that could aid in the digestion of gluten-heavy meals, offering relief to those with non-celiac gluten sensitivity or even individuals looking to maintain a healthier gut microbiota balance. Here’s a brief overview of benefits observed in trials:
- **Gluten degradation:** Enhancement in the breakdown of gluten molecules, making them less inflammatory.
- **Gut health improvement:** Restoration and maintenance of a balanced gut microbiota, crucial for overall health.
- **Inflammatory response reduction:** Lower levels of markers indicating gluten-induced gut inflammation in subjects.
These advancements signify a step forward in dietary management strategies, providing a pathway to better health for individuals navigating the complexities of gluten sensitivities. While the journey from lab to table is long and necessitates further research, the promise exhibited by Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM heralds a future where food choices are no longer limited by the fear of gluten-induced discomfort.
Exploring the Impact of Gluten Additive Food on Mice and the Mitigating Effects of Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM
In recent years, the consumption of gluten has been under scrutiny due to its potential adverse effects on health, particularly for individuals with gluten intolerance and celiac disease. However, a novel approach leveraging the probiotic Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM, known for its gluten-degrading capabilities, presents a promising avenue for mitigating such effects. Research conducted on mice models has shed light on how this probiotic strain not only helps in breaking down gluten in the gut but also plays a crucial role in balancing the gut microbiota. This dual action is pivotal as it opens up possibilities for individuals sensitive to gluten to enjoy a broader range of foods without experiencing negative repercussions.
- Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM’s ability to degrade gluten effectively reduces the presence of this protein, lessening the chances of an adverse reaction in the gut.
- The probiotic’s impact extends to fostering a diverse and balanced gut microbiota, which is essential for overall health and well-being, by outcompeting harmful bacteria and promoting the growth of beneficial microbes.
| Impact Area | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Gluten Degradation | Reduces gluten-related gastrointestinal symptoms |
| Gut Microbiota Balance | Enhances gut health and immune function |
This groundbreaking research paves the way for new dietary supplements that could aid people in managing their gluten intake more effectively, offering a beacon of hope for those grappling with dietary restrictions due to gluten sensitivity.
Recommendations for Incorporating Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM Probiotics to Support Gut Health and Gluten Tolerance
In the quest for maintaining optimal gut health and enhancing gluten tolerance, the introduction of Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM probiotics presents a promising avenue. This distinctive strain not only aids in the decomposition of gluten in the digestive tract, potentially mitigating gluten-associated discomforts but also plays a significant role in balancing the gut microbiota. By fostering a beneficial environment for gut flora, this probiotic strain contributes to improved gastrointestinal health and overall well-being. It’s essential, however, to approach the incorporation of these probiotics with mindfulness to dietary habits and individual health conditions.
For those considering integrating Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM probiotics into their dietary regimen, here are a few recommendations:
- **Consult a healthcare professional**: Before making any significant changes to your diet, a discussion with a healthcare practitioner is advisable to ensure the probiotics align with your specific health needs and dietary restrictions.
- **Start with small doses**: Introduce the probiotics gradually to your diet to assess your body’s tolerance and adapt accordingly, minimizing potential adverse effects.
- **Incorporate probiotic-rich foods**: Alongside supplements, consider including naturally probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables to support gut health diversity.
- **Maintain a balanced diet**: Ensure your overall diet is rich in fibers, vitamins, and minerals to support the efficacy of the probiotics and promote gut health.
Adhering to these guidelines can help individuals reap the benefits of Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM probiotics, potentially easing gluten-related symptoms and contributing to a balanced gut microbiome for improved health outcomes.
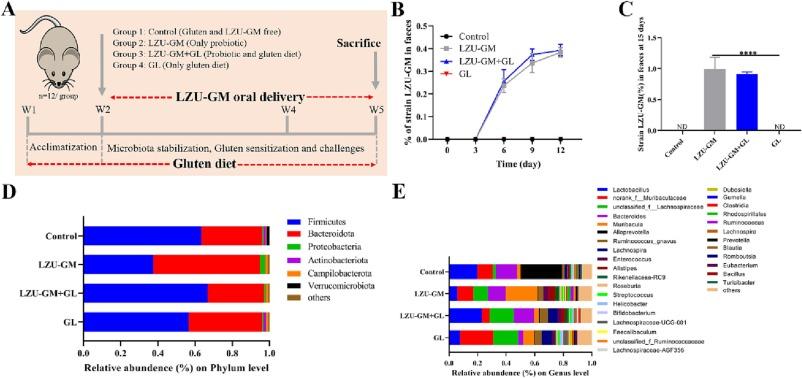
Analyzing the Effects of Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM on Gut Microbiota Balance in Gluten-Fed Mice
In recent times, the consumption of gluten-rich foods has seen a stark rise, bringing to light various adverse health impacts associated with gluten sensitivity and intolerance. Among various strategies employed to mitigate these effects, the spotlight has turned towards probiotics’ potential in restoring gut health balance perturbed by gluten. Particularly, the strain Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM has garnered attention for its unique ability to degrade gluten and ameliorate its adverse effects. Studies conducted on gluten-fed mice revealed that administration of this probiotic strain significantly improved gut microbiota composition, paving the way towards promising applications in gluten-related disorders.
The experiment involved gluten-fed mice, divided into two groups: one receiving Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM and the other, a placebo. Over the course of the study, fecal samples were analyzed to assess changes in the gut microbiota. The findings were remarkable; mice treated with Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM exhibited a balanced gut microbiota characterized by an increase in beneficial bacteria and a decrease in pathogenic microbes. This contrasted sharply with the placebo group, which showed no significant improvements. The table below highlights the significant shifts in microbial populations observed:
<table class="wp-table">
<tr>
<th>Microbial Population</th>
<th>Control Group</th>
<th>Treated with B. subtilis LZU-GM</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Beneficial Bacteria</td>
<td>Low</td>
<td>High</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Pathogenic Microbes</td>
<td>High</td>
<td>Low</td>
</tr>
</table>This dichotomy underscores the capability of Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM not only to degrade gluten effectively but also to catalyze a harmonious balance within the gut microbiota, potentially offering a lifeline to those grappling with gluten-induced health issues.
Q&A
### Q&A: Exploring the Impact of Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM on Gluten-Digestive Challenges
Q1: What is the primary focus of the recent study on Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM?
A1: The primary focus of the study is to explore the effectiveness of a gluten-degrading probiotic, Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM, in mitigating the adverse effects of gluten-containing foods and balancing gut microbiota in mice. The research aims to offer insights into potential dietary interventions for individuals with gluten sensitivities or intolerances.
Q2: How was the study conducted to assess the impact of Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM on mice?
A2: The study involved feeding mice a diet supplemented with gluten, along with the administration of Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM. Researchers monitored the mice for indications of gastrointestinal distress, immune responses, and changes in the gut microbiota composition, comparing these findings against a control group.
Q3: What were the significant findings of the research regarding the health of mice?
A3: Significant findings from the study indicated that mice administered with Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM exhibited reduced adverse effects commonly associated with gluten consumption, such as gastrointestinal inflammation and dysbiosis of gut microbiota. Additionally, these mice showed signs of a more balanced gut microbiome, which suggests a protective role of the probiotic against gluten-induced disturbances.
Q4: How does Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM alleviate the adverse effects of gluten in mice?
A4: Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM likely alleviates the adverse effects of gluten by breaking down gluten molecules before they can induce an inflammatory response in the gut. This action helps to prevent the onset of discomfort and the disruption of gut microbial balance, thereby supporting overall digestive health in the mice.
Q5: Can the findings of this study be applied to humans suffering from gluten-related disorders?
A5: While the findings from this study are promising, it is essential to approach the application to humans with caution. Further clinical trials in humans are necessary to conclusively determine the efficacy and safety of Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM as a dietary supplement for individuals with gluten sensitivities or celiac disease.
Q6: What does the research suggest about the potential for probiotics in managing gluten-related health issues?
A6: The research suggests that probiotics, particularly gluten-degrading ones like Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM, hold potential in managing gluten-related health issues by mitigating the adverse effects of gluten consumption and promoting a healthy balance of gut microbiota. This opens new avenues for dietary strategies aimed at improving the quality of life for individuals with gluten intolerances.
Q7: Are there any limitations to the study that should be considered?
A7: Yes, the study’s limitations include its experimental basis on mice which may not fully replicate human physiological responses to gluten and probiotics. Additionally, the long-term effects and optimal dosage for human consumption of Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM require further research to be fully understood.
This research underscores the importance of exploring innovative dietary interventions and the potential role of specific probiotics in alleviating food-related health challenges.
Closing Remarks
In conclusion, the study on “A Gluten Degrading Probiotic Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM Relieve Adverse Effect of Gluten Additive Food and Balances Gut Microbiota in Mice” signifies a potential breakthrough in dietary management and health solutions for individuals sensitive to gluten. By exploring the capabilities of Bacillus subtilis LZU-GM, this research not only offers hope for mitigating the adverse effects of gluten consumption but also opens the door to understanding the intricate balance of gut microbiota and its impact on overall health. As with all scientific inquiries, further studies and clinical trials are essential to validate these findings and assess their applicability in human subjects. Nonetheless, this study represents a promising step toward advancing our comprehension of probiotics’ role in nutrition and gut health, potentially leading to innovative treatments and dietary recommendations.


